How to Increase AMH Levels: A Comprehensive Guide to Boost Your Ovarian Reserve

Your ovarian reserve plays a critical role in your fertility journey, and anti mullerian hormone levels are an important marker of ovarian health. If you’re trying to conceive or understand your reproductive health, knowing how to increase or support AMH levels is key. This guide provides practical steps, natural remedies, and medical insights to help you navigate this journey confidently.
Understanding AMH & Reproductive Health
What is AMH and its role in reproductive health?
Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) is a glycoprotein produced by your ovarian follicles and a critical indicator of your ovarian reserve – essentially, the number of eggs you have left.
AMH levels reflect the quantity of eggs in the ovaries, making it an essential measure in fertility assessments. It’s used by fertility specialists to evaluate a person’s reproductive potential and tailor treatments accordingly.
Understanding your AMH levels is an essential step in taking control of your fertility journey, especially if you’re considering pregnancy now or in the future. Higher levels often signify a greater number of eggs, while lower levels may indicate a Diminished Ovarian Reserve (DOR).
AMH can also vary based on other factors like age and lifestyle choices, so it’s important to have a complete picture of your fertility health.

How AMH Levels Impact Fertility
Your AMH levels can influence your ability to conceive. Higher levels often signify a greater number of eggs, while lower levels, associated with diminished ovarian reserve and egg health, may present challenges. Low AMH doesn’t mean pregnancy is impossible – many women with low AMH conceive with the help of fertility treatments. However, it can make it more challenging to conceive naturally without medical intervention. Understanding these nuances can help you make informed decisions about your fertility options.
Causes & Symptoms of Low AMH Levels
Potential Causes of Low AMH Levels
Several factors can influence AMH levels, including:
- Aging: Natural decline in ovarian reserve with age. This is the most common cause of low AMH, as the pool of follicles reduces over time.
- Lifestyle: Smoking, poor diet, and high BMI can reduce AMH levels. A diet high in processed foods, excessive sugar, and unhealthy fats can contribute to hormonal imbalances, which in turn affect AMH levels.
- Environmental Toxins: Exposure to pollutants and harmful chemicals, such as BPA in plastics, pesticides, and certain cosmetics, can impact ovarian health and AMH production.
- Medical Conditions: Disorders like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and autoimmune diseases can alter AMH production. These conditions often lead to irregular menstrual cycles, hormone imbalances, and a reduced ovarian reserve.
Symptoms of Low AMH levels
While low AMH levels don’t always show outward signs, potential symptoms include:
- Irregular or absent menstrual cycles: This is a common symptom indicating reduced ovarian function.
- Difficulty conceiving despite regular attempts: Lower AMH levels may indicate fewer viable eggs, making it harder to conceive naturally.
- Menopausal-like symptoms at an earlier age: Women with significantly reduced ovarian reserves may experience symptoms associated with menopause, such as hot flashes and night sweats, earlier than average.
Understanding AMH Test Results
AMH levels are measured via a simple blood test that can be done at any point in the menstrual cycle. These results provide insights into your ovarian reserve and fertility potential. Typical AMH levels vary by age:
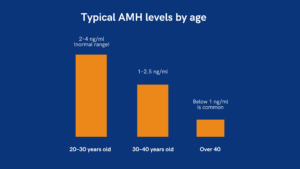
Levels below 0.9 ng/mL are considered low, and anything below 0.16 ng/mL is classified as ‘undetectably low’. Fluctuations in AMH levels can suggest various fertility concerns in women.
AMH levels naturally decline with age, and a notably low level for a woman’s age could indicate an increased risk of early menopause. On the other hand, exceptionally high AMH levels might suggest the presence of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). It’s important to note that while the test provides a count of remaining eggs, it doesn’t evaluate their quality or health. This information should be considered alongside other fertility measures for a more comprehensive understanding of ovarian health.
While AMH levels naturally decline with age, there are steps you can take to support ovarian health. This involves adopting a holistic approach that includes diet, lifestyle, and supplements, though significant increases are unlikely. The focus should be on maintaining overall fertility and egg quality.
Natural Ways to Support AMH Levels & Ovarian Function
Balanced Diet & Foods that Support Ovarian Health
A nutrient-rich diet can boost overall fertility health and ovarian function. Include foods such as:
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and arugula for antioxidants that protect ovarian cells from oxidative stress, a known contributor to reduced AMH levels.
- Healthy fats: Avocados and nuts for hormonal balance, including estrogen and progesterone, which play a key role in fertility.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Salmon and flaxseeds for cell health and reducing inflammation, which is crucial for optimal ovarian function.
- Vitamin D-rich foods: Fortified milk and mushrooms, as Vitamin D is linked to improved ovarian function and egg quality. Sun exposure can also boost Vitamin D levels.
- Berries: Eating berries regularly can give you a good dose of antioxidants, which can help protect your eggs from damage.
Avoid processed foods, excessive sugar, and trans fats, as these can negatively impact your ovarian reserve and AMH levels.
Healthy Lifestyle & Habits that Impact Ovarian Reserve
- Exercise Regularly: Moderate physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and hormonal balance. Excessive exercise without adequate recovery can lead to reduced AMH levels due to increased cortisol, a stress hormone that can impact ovarian health.
- Keep Your Stress Under Control: High stress levels can interfere with the hormonal balance necessary for conception. Activities such as yoga, mindfulness, or journaling can lower stress-induced hormonal imbalances, which in turn can support AMH levels.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking accelerates egg loss and decreases AMH levels. Quitting smoking can have a positive impact on your ovarian reserve.
- Limit Environmental Toxins: Reduce exposure to chemicals in plastics, pesticides, and cosmetics. Opt for organic produce, use BPA-free containers, and choose chemical-free beauty products.
Supplements and Fertility
Supplements like Vitamin D, CoQ10, Omega-3s, and DHEA have been shown to support ovarian function. CoQ10, an antioxidant, is particularly beneficial as it helps protect ovarian cells from damage and may improve egg quality. DHEA, a hormone precursor, can help increase AMH levels in women with diminished ovarian reserves. Omega-3 fatty acids can reduce inflammation and improve blood flow to the ovaries, enhancing egg quality. Consult a fertility specialist before starting any supplement regimen to ensure they are appropriate for your individual needs and conditions.
H2: Fertility Treatments and Medical Options for Low AMH Levels
Conceiving with low AMH levels can be challenging, but it is not impossible. Low AMH indicates a reduced ovarian reserve, which means fewer eggs are available for fertilization. This can make natural conception more difficult, but several strategies and medical options can help increase the chances of pregnancy.
Natural Conception
For women with low AMH, achieving pregnancy through natural means can be more difficult but not out of reach. The key is to maximize the chances of conception by having intercourse during the most fertile periods of the menstrual cycle. Tracking ovulation through methods like basal body temperature monitoring, ovulation predictor kits, and cervical mucus observation can help identify the optimal time to conceive. Couples may also consider lifestyle changes to improve fertility, such as maintaining a healthy weight, reducing stress, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol use.
Medical Interventions
When natural conception is not successful, medical interventions can be considered. Fertility medications, such as Clomid (clomiphene citrate) or Letrozole, may be prescribed to stimulate the ovaries and encourage the release of a healthy egg. These medications can be used in conjunction with other treatments, like intrauterine insemination (IUI), where sperm is directly placed into the uterus around the time of ovulation to improve the chances of fertilization.
IVF and Egg retrieval
For individuals with low AMH levels, In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is often the preferred fertility treatment due to its ability to maximize egg retrieval and enhance the chances of conception. IVF involves the stimulation of the ovaries with medications to produce multiple eggs, even when the ovarian reserve is limited. The goal is to achieve a controlled ovarian hyperstimulation, which can help overcome the challenge of low AMH levels and improve the chances of retrieving several eggs during the egg retrieval process.
To optimize outcomes for women with low AMH, IVF protocols are specifically tailored to increase the number of eggs retrieved. This customization includes adjusting the dosage of fertility medications to stimulate the ovaries more effectively and closely monitoring the response to these medications. Advanced monitoring technologies, such as ultrasound and blood tests, are used to track the development of follicles and ensure the best possible response to treatment.
Advanced Technologies
IVF techniques have advanced significantly over the years, providing additional options to enhance success rates. Embryo freezing is one such technology that allows for multiple cycles of IVF. By freezing surplus embryos, couples can avoid the need for fresh cycles each time they attempt conception. This approach not only increases the chances of pregnancy but also offers a backup plan if initial cycles are unsuccessful.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing of embryos can significantly improve the likelihood of a successful pregnancy for those with low AMH levels. Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT), also known as genetic screening, allows for the identification of genetic disorders and chromosomal abnormalities in embryos before implantation. This process helps in selecting the healthiest embryos, reducing the risk of genetic conditions in the baby and increasing the chances of a healthy live birth.
Donor Eggs
In cases where AMH levels are extremely low and other methods are not effective, using donor eggs may be an option. Donor eggs can provide a higher number of eggs and better egg quality, increasing the likelihood of a successful pregnancy. This option allows couples to have a genetically related child, and it can be a viable choice for those who want to pursue parenthood despite challenges with their own ovarian reserve.
Low AMH Levels? Take the Next Step in Your Fertility Journey
Low AMH doesn’t mean the end of your fertility journey. Understanding your options – from natural methods to advanced treatments – can help you take control.
The journey to parenthood with low AMH levels may require patience, perseverance, and the right combination of medical interventions and lifestyle changes. With the right approach, many women and couples are able to achieve their dream of becoming parents. Consulting with a fertility specialist who can provide personalized guidance and support is crucial to developing a tailored treatment plan that aligns with individual goals and circumstances.
Schedule a consultation with our fertility clinic to explore personalized solutions and keep hope alive.
Your Low AMH Questions Answered
What are normal AMH levels?
AMH levels vary with age, typically ranging from 1.0–4.0 ng/ml for women of reproductive age. Levels below this range indicate a diminished ovarian reserve.
How does AMH affect fertility potential?
Higher levels indicate greater ovarian reserve, but low levels don’t rule out conception. Many women with low AMH levels conceive with the help of fertility treatments and lifestyle changes.
Can AMH levels fluctuate?
Yes, AMH levels can fluctuate, although they are generally considered to be stable markers of ovarian reserve over time. However, several factors can influence AMH levels and cause minor variations, such as hormonal changes, age, medication and treatments, diet and lifestyle.
Why did my AMH drop so quickly?
While AMH cannot be drastically increased, lifestyle changes (such as improving diet, quitting smoking, reducing stress) and supplements may support ovarian health and slow the decline of AMH levels.
How many eggs do I have left if my AMH is low?
Low AMH provides an estimate but doesn’t specify the exact number of eggs. Further testing (like an antral follicle count) can give a clearer picture.
Can I conceive with low AMH?
Yes, many women with low AMH conceive naturally or with fertility treatments. The key is to work closely with a fertility specialist who can recommend personalized strategies to optimize your chances.
What AMH level is too low for pregnancy?
There isn’t a universal “too low” level, but AMH levels below 0.5 ng/ml often indicate a significantly reduced ovarian reserve. Even so, successful pregnancy is still possible with medical assistance.
What do low AMH levels mean for my chances in IVF?
Research shows that IVF results in patients with very low serum AMH are significantly affected by age.
If you’re younger (typically, under 35), low but measurable AMH levels shouldn’t be a major concern. Medication will be prescribed to stimulate your body to produce follicles, which are likely to be of good quality given your younger age. Remember, low AMH doesn’t necessarily mean low-quality eggs; it simply indicates a lower quantity, which is less critical when undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART).
However, if you have undergone cancer treatments or experience early-onset menopause, your AMH levels may be virtually non-existent, making pregnancy difficult.
For those older than 35 with low AMH, the chances of success in IVF are significantly reduced, as demonstrated by research. This doesn’t mean that pregnancy is impossible, but it does considerably decrease the likelihood of a successful outcome.
Can you retrieve eggs with low AMH?
Yes, eggs can often be retrieved even with low AMH levels. IVF protocols can be tailored to stimulate egg production and maximize retrieval success.
Can I increase my AMH levels?
While AMH levels cannot be dramatically increased, supporting ovarian health through lifestyle changes, proper nutrition, and supplements may help. Fertility treatments can also address low AMH levels effectively.
Which food increases AMH level?
Foods rich in Vitamin D, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids may support ovarian health. Examples include salmon, walnuts, leafy greens, and fortified dairy products.
How can I increase my AMH level fast?
There is no guaranteed quick fix for increasing AMH levels. However, adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, taking fertility-supportive supplements (like CoQ10 and Vitamin D), and consulting with a specialist can help optimize fertility in the short term.